16 MAY 2025
Compressed Natural Gas Fueling Stations
Designs, technologies, and use cases of CNG fueling stations for public and private fleets.
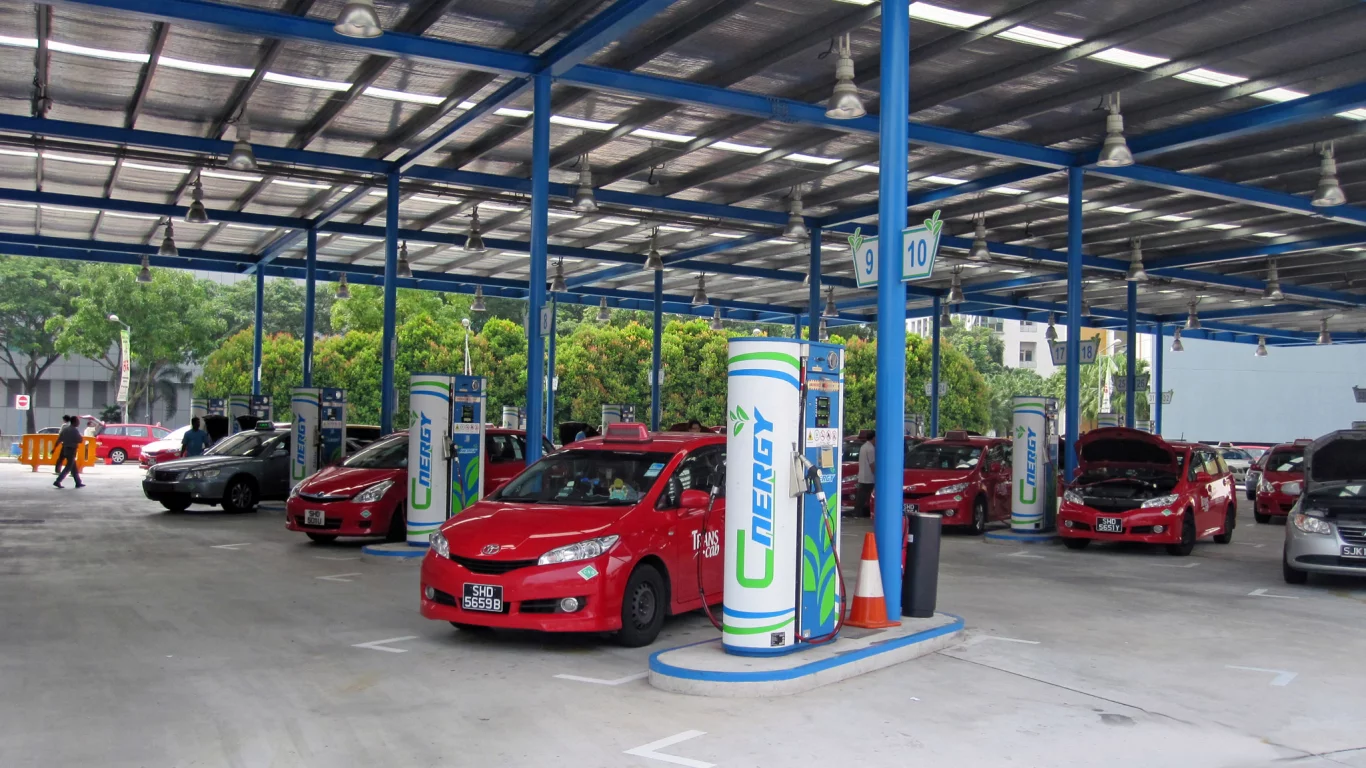

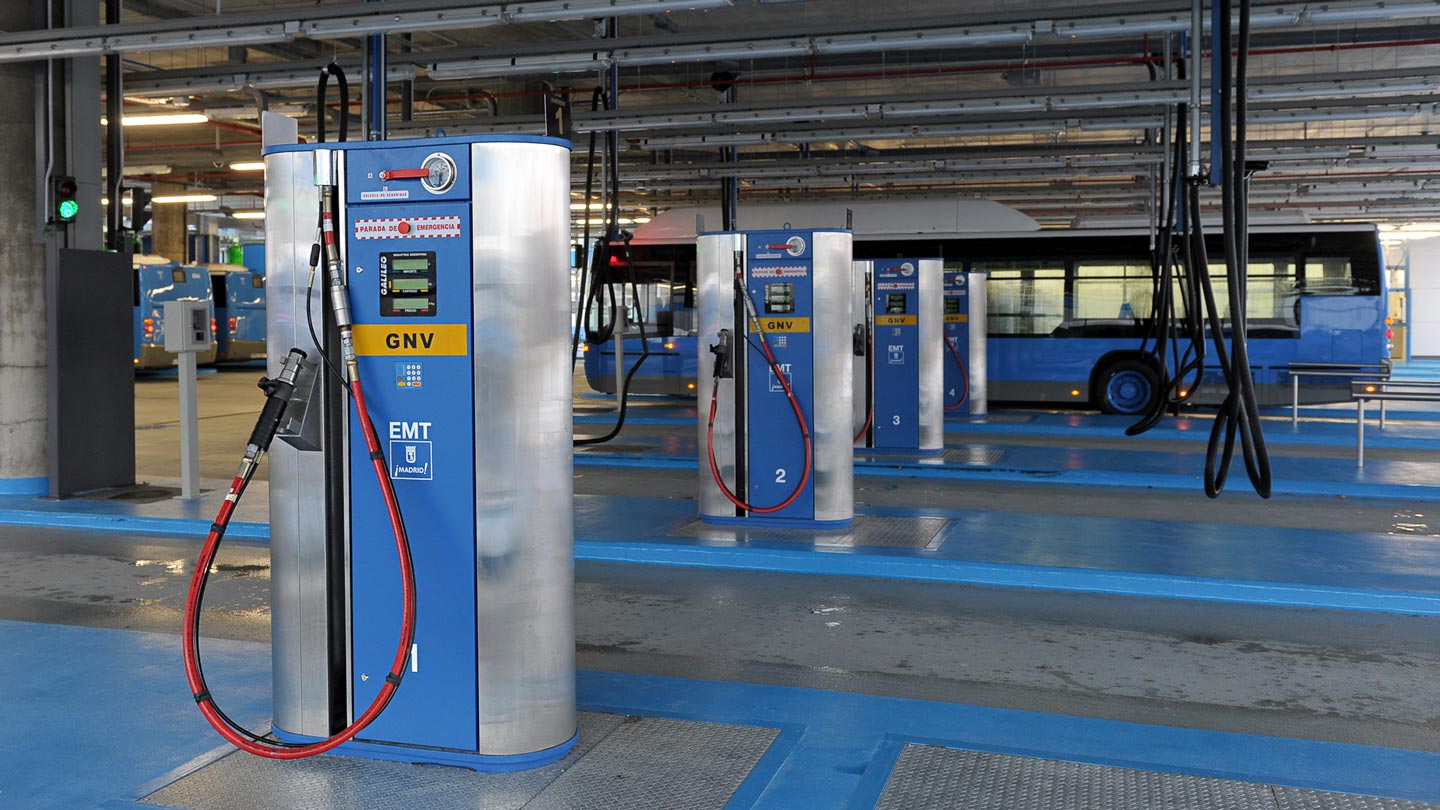
CNG fueling station, Singapore.
Whar are CNG Fueling Stations | Types of CNG Fueling Stations | How Do CNG Fueling Stations Work? | Real-World Example
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) fueling stations are specialized facilities designed to dispense natural gas at high pressures for vehicular use. Nearly half of all CNG stations are private, accessible only to fleet operators.
Unlike conventional gasoline or diesel stations, CNG fueling stations must be tailored to meet specific operational requirements. This involves carefully balancing compressor capacity, storage volume, and operating pressure to ensure optimal performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
What Are CNG Fueling Stations?
A CNG station typically receives natural gas at low pressure from a local utility line, compresses it on-site, and stores it until needed for refueling.
Because users have different volume demands and refueling speed requirements, there is no universal CNG station design that fits all needs.
For example, companies like Galileo offer a range of modular compression solutions, including the Nanobox NX, Microbox MX200, and Gigabox MX400. In the case of biogas, advanced conditioning systems—such as the Biobox 1000-1500 HP—are used to transform raw biogas into biomethane, making it suitable for use as vehicle fuel. Choosing the right system impacts fuel costs and vehicle range.
- For large vehicles (buses, trucks): A Gigabox system provides higher throughput, ensuring an efficient fueling process.
- For passenger cars: Compact units like Nanobox or Microbox offer a practical, space-efficient solution.
- Plug-and-play flexibility: All these solutions are designed for quick installation and minimal infrastructure requirements.
More than 25% of CNG fuel dispensed in Europe in 2020 was bio-CNG, and over 4,400 stations now offer biomethane at the pump. cng-mobility.ch
Types of CNG Fueling Stations
CNG stations come in three main configurations—fast-fill, time-fill, and combination-fill—each designed to meet different operational needs.
Fast-Fill Stations
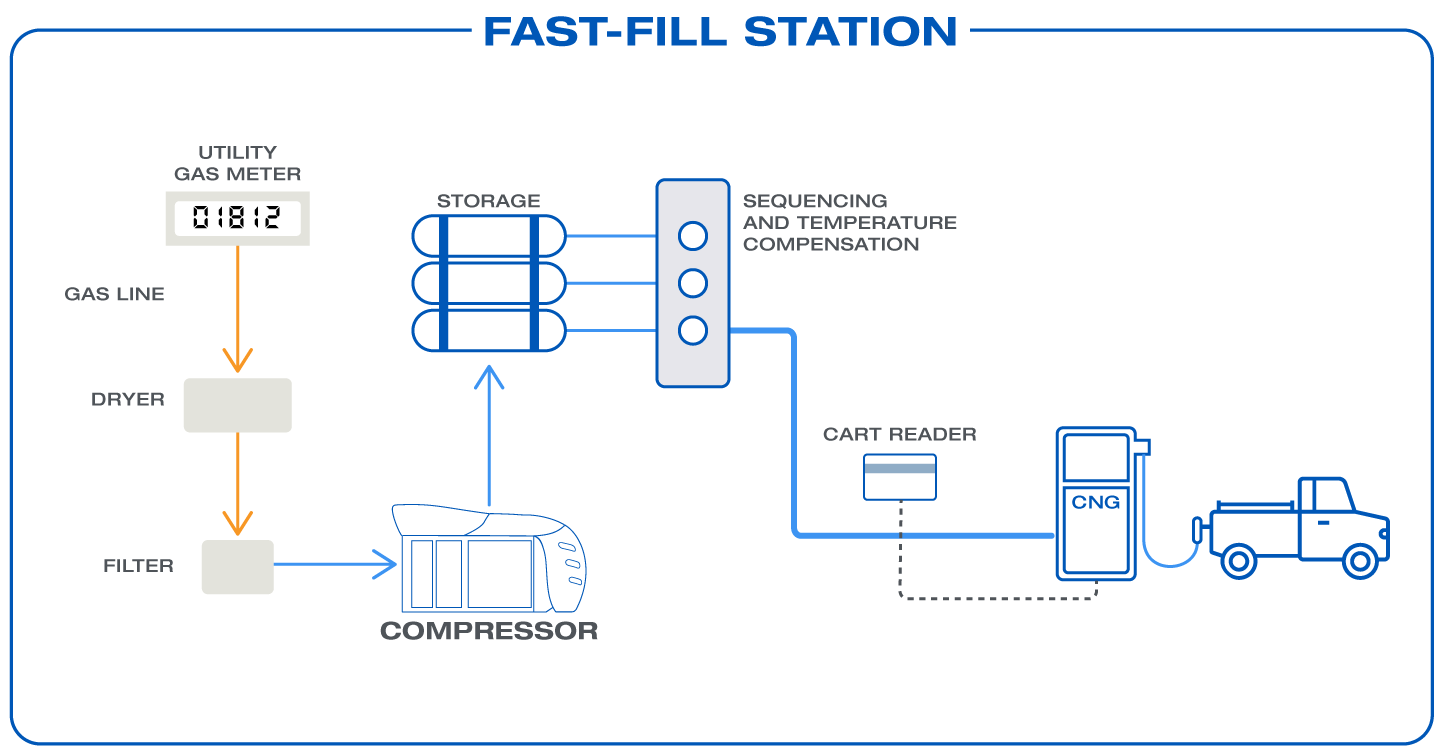
Fast-fill stations serve locations where vehicles arrive unpredictably and need quick refueling—similar to conventional gas stations.
- Process: Natural gas is compressed to a high service pressure (typically 4,300 psi) and stored in pressure vessels, ensuring rapid dispensing.
- Operation: Advanced sensors monitor both pressure and temperature for precise fueling. Modular solutions such as Nanobox, Microbox, or Gigabox allow for scalable capacity while maintaining a compact footprint.
- Use Case: Ideal for public CNG stations or fleet operations where speed is critical.
All public CNG stations use fast-fill systems, allowing vehicles to refuel in minutes, just like at a gasoline pump. afdc.energy.gov
Time-Fill Stations
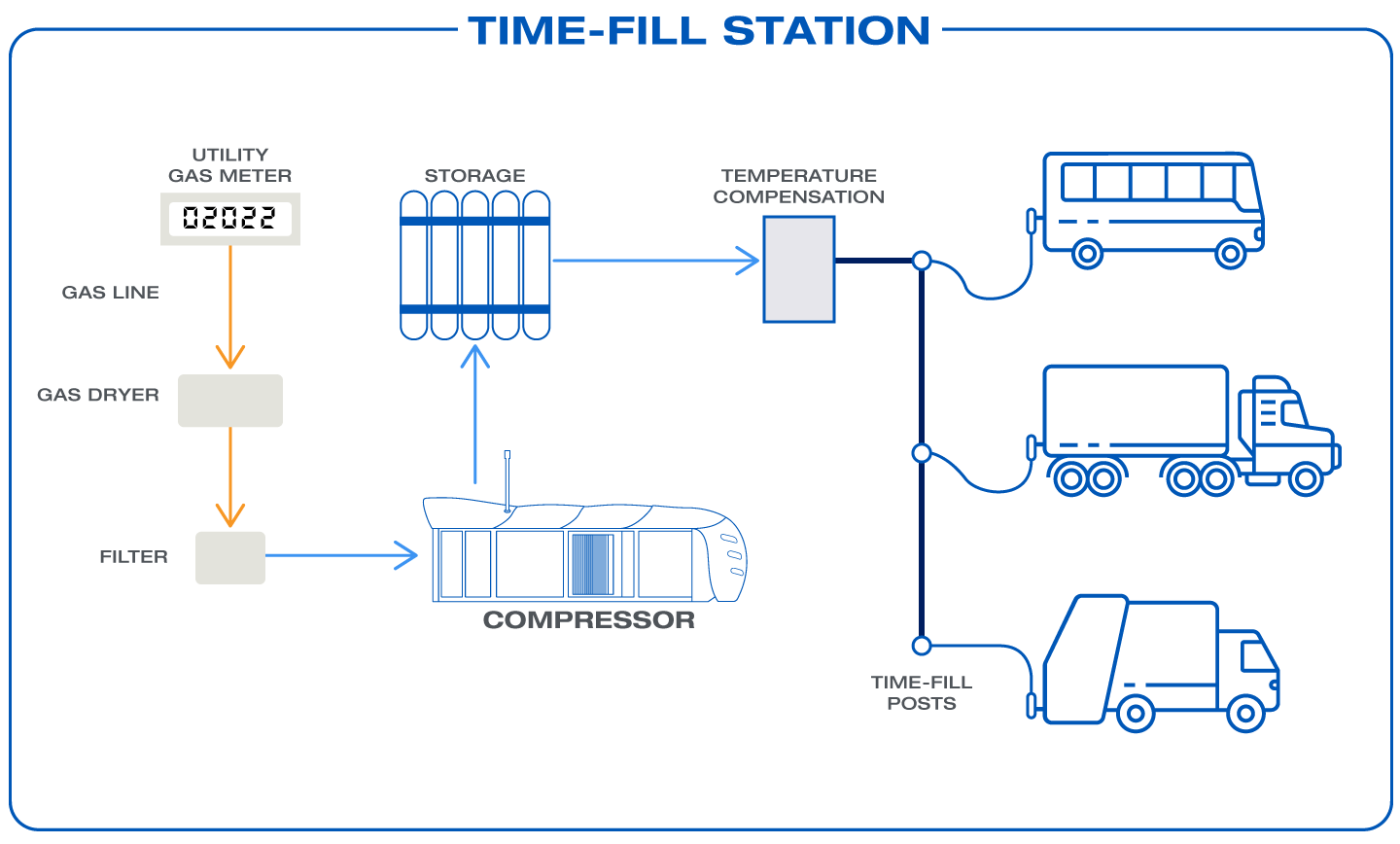
Time-fill (or slow-fill) stations are designed for fleet operations where vehicles can refuel gradually—typically overnight.
- Process: A Microbox MX200 or Microskid MX200 compressor draws low-pressure gas from the utility line and delivers it directly to vehicles at a slower rate.
- Operation: Refueling may take several hours, but the reduced heat of compression allows for a more complete fill. Small buffer storage tanks help regulate the compressor, minimizing wear and tear.
- Use Case: Ideal for fleets—such as buses and trucks—that refuel outside peak hours, lowering electricity costs and ensuring hassle-free operation.
Time-fill stations primarily serve fleet vehicles, requiring little storage but longer fueling times. afdc.energy.gov
Combination-Fill Stations
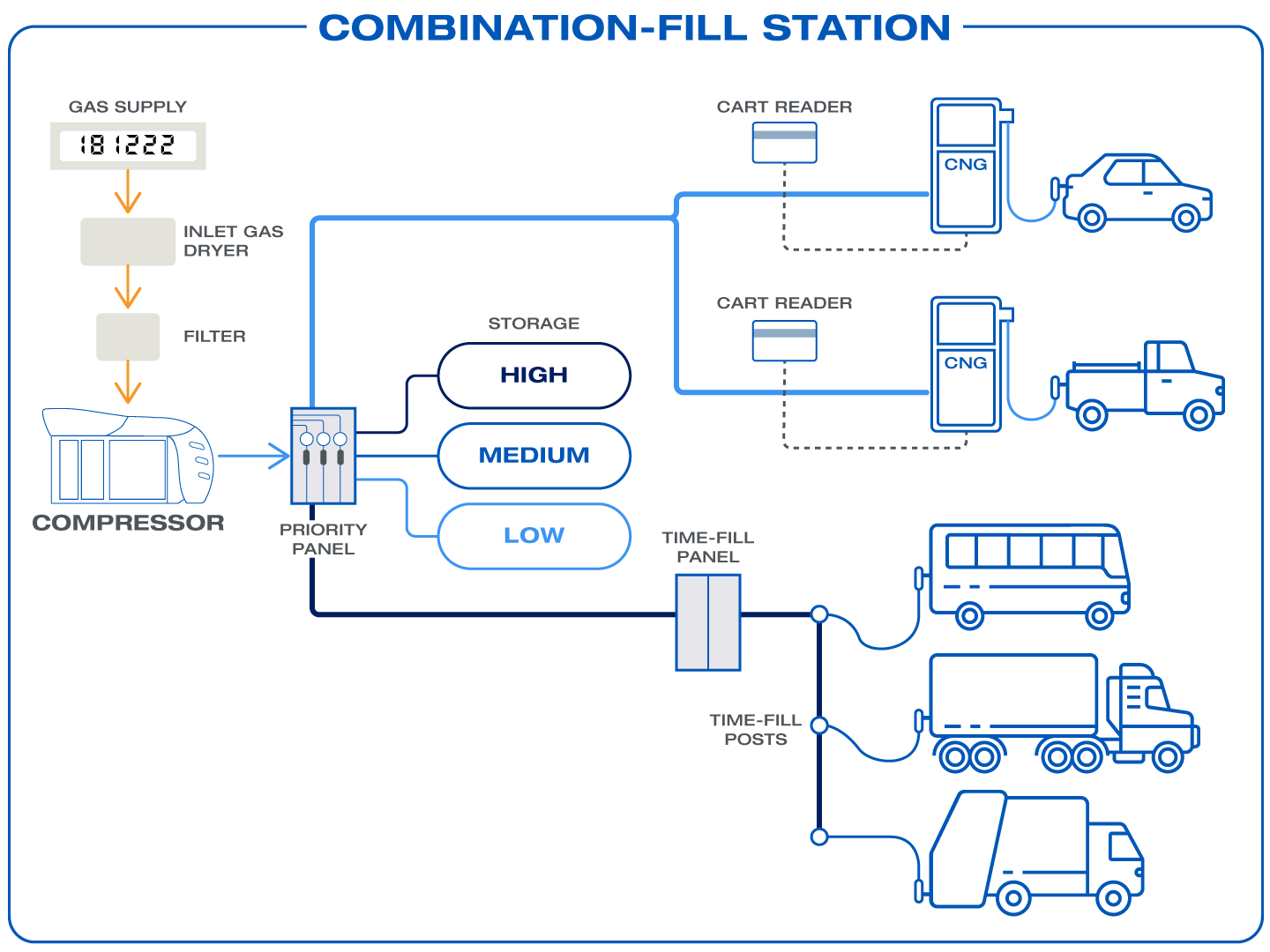
Combination-fill stations integrate both fast-fill and time-fill capabilities into a single system.
- Process: Overnight fleet vehicles connect to time-fill posts, while others can use a fast-fill dispenser for quick top-ups.
- Operation: A higher-capacity compressor, such as the Microbox MX400 or Microskid MX400, can power both systems. Galileo’s EMB dispenser enables precise, flexible fuel dispensing.
- Use Case: Perfect for mixed fleets, serving both long-haul trucks that need fast refueling and local fleets that can refuel overnight. If a Gigabox system is installed, the station can support both private and public fueling.
How Do CNG Fueling Stations Work?
Regardless of station type, several key steps ensure efficient CNG operations:
- Needs Assessment: Engineers analyze fuel demand, vehicle tank sizes, and throughput requirements. If biomethane conditioning is needed, systems like ZPTS - Molecular Sieve or Amines are integrated to purify the gas before compression.
- System Design: Stations are customized based on site constraints, balancing compressor power, storage volume, and necessary gas treatment. A Biobox 250–1500 can be combined with a Microbox or Nanobox to ensure fuel quality and optimal compression.
- Installation: Modular, plug-and-play systems—such as Galileo’s Gigabox or Microbox—arrive preassembled, reducing installation time and on-site construction.
- Monitoring & Maintenance: Remote monitoring systems detect performance and safety issues in real time, while regular servicing keeps compressors, dispensers, and components running efficiently.
Real-World Example: Galileo’s Modular Solutions
From public refueling stations to private fleets, Galileo Technologies offers modular solutions for rapid deployment and scalable capacity.
Key Solutions:
- Gigabox – High-throughput CNG fueling for large-scale operations.
- Microskid MX200 & MX400 – Adaptable compression systems for various industries.
- Nanobox & Microbox – Compact, efficient units for small-scale stations.
- EMB Dispensers – Smart, precision-fueling technology.
- Biobox Series – Advanced conditioning systems ensuring fuel purity.
Environmental Impact:
- Studies in Switzerland show that CNG cars emit 15–20% less CO₂ than gasoline vehicles (research-collection.ethz.ch).
- According to EPA data, natural gas reduces greenhouse gas emissions by 6–11% per mile compared to gasoline (nccleantech.ncsu.edu).
Conclusion
CNG fueling stations are highly specialized installations that require careful design, planning, and system integration to suit the end user’s needs.
- Selecting the right station type—fast-fill, time-fill, or combination-fill—ensures efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Incorporating the right equipment for compression and gas treatment maximizes performance and fuel quality.
- Companies like Galileo demonstrate how modular, scalable solutions—ranging from Nanobox and Microbox to high-capacity Gigabox and Microskid—allow station owners to scale operations based on current needs and future growth.
As the global push for cleaner transportation accelerates, CNG remains a key player in sustainable mobility. Studies confirm that modern CNG stations are safe, efficient, and environmentally beneficial, with ongoing advancements—such as better compressors and increased use of renewable gas—enhancing performance (cordis.europa.eu & cng-mobility.ch).
Key Takeaway:
CNG fueling stations offer a cost-effective, lower-emission alternative to traditional fuels. By choosing the right station setup and advanced modular technology, businesses and governments can drive the transition to a cleaner, more efficient fueling infrastructure.
Sources
- U.S. DOE Alternative Fuels Data Center – Natural Gas Fueling Station Counts and Types | afdc.energy.gov
- U.S. EIA – Today in Energy report on alt-fuel station availability (2012) | eia.gov
- European Commission / EAFO – Alternative Fuels Observatory (CNG station data portal) | alternative-fuels-observatory.ec.europa.eu
- NGV Magazine / CNG news – Industry reports on CNG network growth | lngprime.com & cng-mobility.ch
- NGVAmerica station map tool coverage | gasbuddy.com
- UK HSE – CNG Refueling FAQ and Gas Safety Regulations | hse.gov.uk
- IGEM – Standard UP/20 for CNG Stations (2022) | igem.org.uk
- CNG Fuels (UK) / EU CORDIS – Mother-Daughter Station Concept Project | cordis.europa.eu
- Clean Energy Fuels – Company Profile (Natural Gas Fueling Stations) | dnb.com
- Academic Studies – ETH Zürich “Optimization of CNG station network” | research-collection.ethz.ch
- NC Clean Energy Tech Center – “How to Implement CNG” | nccleantech.ncsu.edu
- ICCT – NGV Emissions Assessment (2015) | nccleantech.ncsu.edu
